Electrocoagulation Technology

Electrocoagulation Technology for
Sustainable Water Treatment
Delving Blue recognizes the potential of EC technology and has gone one step further by replacing sacrificial electrodes with polarity reversal electrodes to boost the longevity and efficiency of this innovative technology. Integrating it into existing water treatment schemes to provide tailored solutions for specific water quality challenges. By combining novel EC with other advanced treatment processes, we can achieve optimal results and ensure sustainable water management.

How it works?
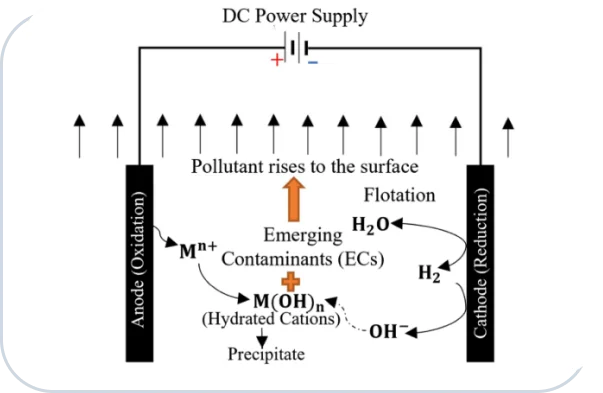
Content: Electrocoagulation (EC) is an advanced electrochemical technology that uses electric currents to remove contaminants from water. In this process, metal ions are released from electrodes and act as coagulants, aggregating pollutants which are then easily removed. EC is recognized for its high efficiency in treating a variety of water streams such as textile, leather, metal, and food industries, etc.
Revolutionizing Water & Wastewater
Treatment with Electrocoagulation
Why EC
- 20-30% less sludge than chemical coagulation
- 10-20% more cost effective
- 9x lower operational cost
- -1-2 kwh/m3 energy use
- Chemical-free, by-product-free
- Conducive to down-stream processes
- Eco-friendly
- Better treatment efficiency
- Lower area footprint
- Versatile and Adaptable
- Retrofit any process flow
- High floc forming efficiency

Applications
| Drinking Water | Industrial Wastewater | Municipal Water |
|---|---|---|
|
Filter Backwash Water Recovery Surface- & Sea-Water Ground Water Both Sweet & Brackish Pre-Treatment To Reverse Osmosis |
Textile Industry (COD, BOD, Color Removal) Leather Industry (Sulfides, Chromium Removal) Metal Surface Treatment (Heavy Metals, Phosphorus Removal) Landfill Leachate (COD, BOD, Color) Oil Emulsion Breaking And Recovery Paper & Pulp Dairy Industry Pharmaceuticals Food & Beverages Livestock Fertilizers Food & Beverages Livestock Greenhouse Industry |
Municipal Water |
Applications
| Feature | Electrocoagulation | Chemical Coagulation |
|---|---|---|
| Sludge Production | Typically produces 20-30% less sludge than chemical coagulation. | Produces 50-70% more sludge than electrocoagulation. |
| Energy Use | Requires approximately 1-2 kWh/m³ of treated water. | Requires minimal energy for chemical dosing, typically less than 0.5 kWh/m³. |
| Operating Cost | Can be 10-20% more cost-effective in the long run due to reduced chemical costs. | Can be 5-15% less expensive in the short term but may have higher long-term costs due to chemical purchases and disposal. |
| Environmental Impact | Generally considered more environmentally friendly, as it avoids the introduction of additional chemicals into the wastewater. | Can have a greater environmental impact due to the use and disposal of chemical coagulants. |
| Treatment Efficiency | Generally comparable to chemical coagulation for many types of pollutants, but may be more effective for certain contaminants, such as heavy metals and organic matter. | Generally effective for a wide range of pollutants, but may be less effective for certain contaminants, such as color or turbidity. |
| Plant Area Requirement | Lowest area requirement as no retention time required for EC. | Needs large area requirement as compared to EC for successful formation of flocs. |
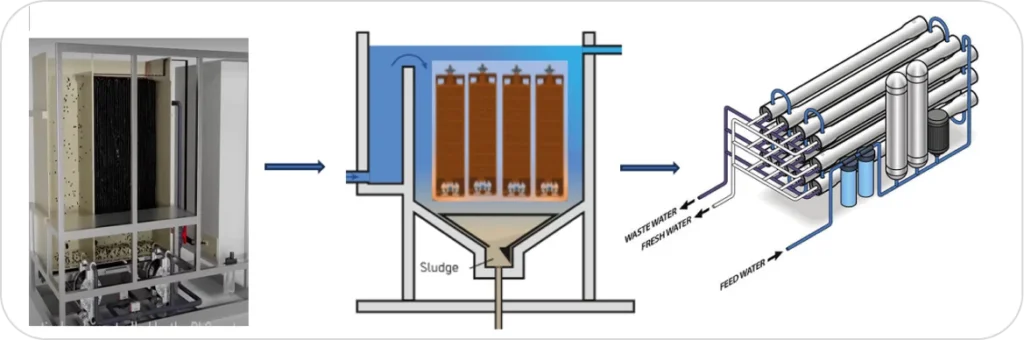
Integrating Electrocoagulation with
our innovative technologies and existing processes
Partner with Us for
Tailored EC Solutions

Electrocoagulation can be tailored to your specific water & wastewater treatment needs. Our expert team will design, build, and implement a customized solution to meet your requirements.








